

It works roughly the same but you need to perform a bit more base-2 magic. You can then translate the binary IP address to a human-readable one. If either or the fields have a 0 then you enter a 0 on the third row. If both the base-2 IP address and the mask have a 1 in a field then you add a 1 in the same field on the last row. That sounds complicated but it is quite easy. The third row calculates what the first IP address is by doing a binary and operation between the first two rows.

Below, the first row is the IP address 84.18.206.207 in base-2 and the second row is the mask. To calculate the first IP address in the range you can use another table.

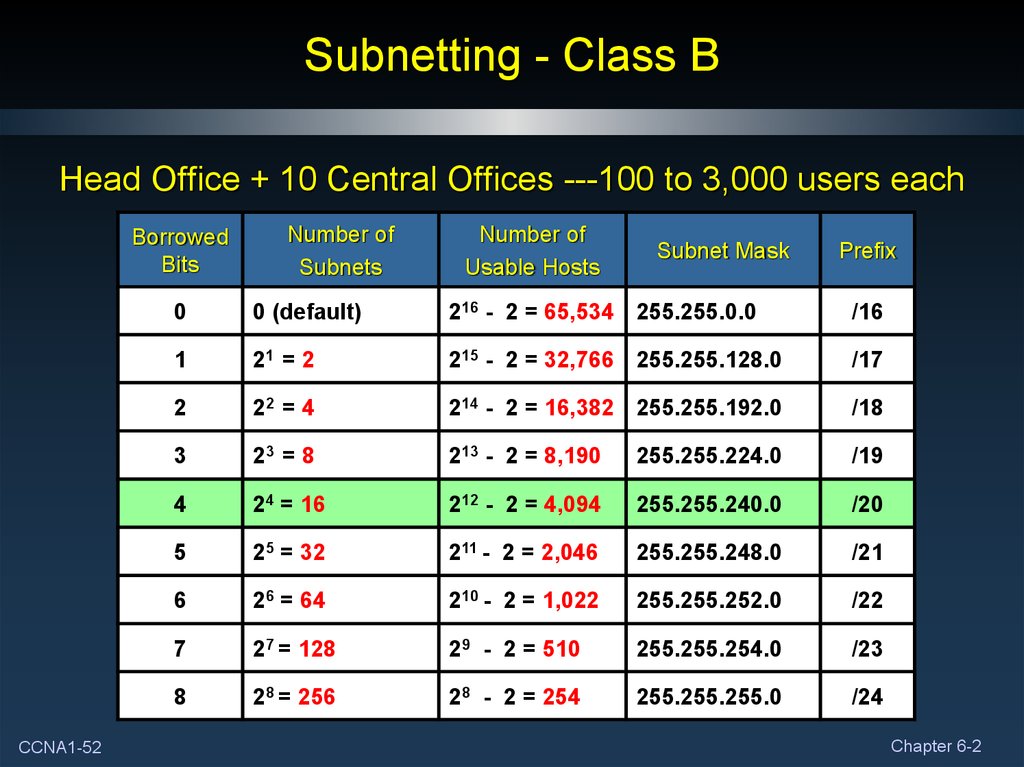
So, in effect a /23 mask gives you 510 usable IPs. Remember, though, that not all 512 IPs can be assigned to nodes, as the first and last IP in the range are reserved. In other words, the calculation is like so: If you are lost here, 9 is an exponent that defines how many times the base number (2) needs be multiplied. So, 2 (32-23) translates to 2 9, or “2 to the power of 9”: We are using 32 because IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, and we are subtracting the number of bits that are turned on (23). But how do you calculate the number of IPs? To do so, we need to brush up on our knowledge of exponents. In other words, the first seven bits in the third octet are turned on in a /23 network. You get to 254 by adding up the first seven columns. To see where the cut-off point is you can draw an exponent table: All bits in the first two octets are turned on (255) and the entire fourth octet are nodes (0). This is a class A IP address, but the mask is used to make the first 23 bits the network part.Īs a quick recap of the article about subnetting and CIDR, the interesting part in this example is the third octet. Calculating the number of IPsįor this article I will use our Strawberry server as an example. To follow along you need to have a good understanding of base-2 numbers. I will explain how you can find the number of IP addresses in a subnet and how you can find the first and last IP address in the range. Since the introduction of CIDRs, however, assigning an IP address to a network interface requires both an address and its network mask.īelow is a table providing typical subnets for IPv4.In my article about subnetting and CIDR I looked at how you can identify what part of an IP address is part of the network. Prior to the introduction of CIDR, IPv4 network prefixes could be directly obtained from the IP address based on the class (A, B, or C, which vary based on the range of IP addresses they include) of the address and the network mask. In IPv6, the network prefix performs a similar function as the subnet mask in IPv4, with the prefix length representing the number of bits in the address. In IPv4, these subnet masks are used to differentiate the network number and host identifier. All hosts on a subnetwork have the same network prefix, unlike the host identifier, which is a unique local identification. For IPv4, networks can also be characterized using a subnet mask, which is sometimes expressed in dot-decimal notation, as shown in the "Subnet" field in the calculator. CIDR is a method used to create unique identifiers for networks, as well as individual devices. A routing prefix is often expressed using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation for both IPv4 and IPv6. A rest field is an identifier that is specific to a given host or network interface. IPv4 is the most common network addressing architecture used, though the use of IPv6 has been growing since 2006.Īn IP address is comprised of a network number (routing prefix) and a rest field (host identifier). The act of dividing a network into at least two separate networks is called subnetting, and routers are devices that allow traffic exchange between subnetworks, serving as a physical boundary. It is commonly known as TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol). Related Bandwidth Calculator | Binary CalculatorĪ subnet is a division of an IP network (internet protocol suite), where an IP network is a set of communications protocols used on the Internet and other similar networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
